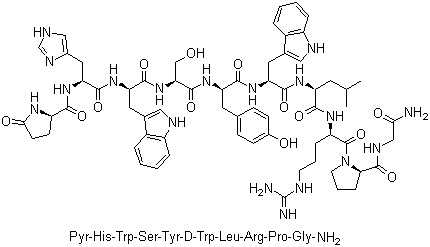
Triptorelin(CAS#57773-63-4)
Risk and Safety
| Hazard Symbols | T – Toxic |
| Risk Codes | 60 – May impair fertility |
| Safety Description | S53 – Avoid exposure – obtain special instructions before use. S22 – Do not breathe dust. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2937190000 |
Triptorelin(CAS#57773-63-4) Information
anti-tumor drugs The active ingredient of triptorelin is an analog of synthetic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), also known as methorelin, Daphne, Dabija, and Gonarelin. It is an anti-tumor drug with the same pharmacological effects as Goserelin and Buserelin, its structural improvement is to replace the sixth L-glycine in the natural molecular structure with D-tryptophan, making its promoting effect more significant and the plasma half-time longer, with higher drug efficacy. After intramuscular injection, the pituitary gland will initially be stimulated to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle maturation hormone (FSH). When the pituitary gland enters the refractory period after long-term stimulation, the release of gonadotropins is reduced, thereby reducing the sex hormones to castration levels. The above effects are reversible. Subcutaneous drug absorption is rapid, Tmax is 15min,1h to reach the maximum effect, sustained-release preparation intramuscular injection can maintain the efficacy of more than 28 days. Clinically, it is mainly used to treat endometriosis, hormone-dependent prostate cancer, breast cancer, and true precocious puberty in children. It can also be used for assisted reproductive technology. The main adverse reactions of tripferelin are as follows: urinary disorders, breast swelling and pain, bone pain, etc. may occur in the early stage of male treatment, as well as hot flashes, loss of libido and impotence. Male and female breasts, testicular atrophy and sleep disorders are rare. There will be a small amount of vaginal bleeding in girls during the first week of treatment in children, which can be corrected by short-term additional treatment. Hot flashes, bleeding or bleeding spots, vaginal dryness, headache and weakness may occur during women’s treatment. Combined use of gonadotropins can cause abdominal and/or pelvic pain. Because the concentration of estrogen is reduced to the postmenopausal level, it can cause slight loss of trabecular matrix. Generally, it can return to normal six to nine months after treatment is stopped. Patients with endometriosis may have irreversible amenorrhea after medication.