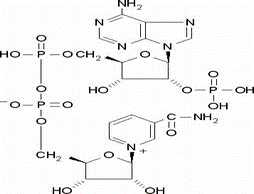
Triphosphopyridine nucleotide(CAS# 53-59-8)
| Hazard Symbols | Xi – Irritant |
| Risk Codes | 36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36 – Wear suitable protective clothing. |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UU3440000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 10-21 |
Introduction
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, also known as NADP (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), is an important coenzyme. It is ubiquitous in cells, involved in many biochemical reactions, and plays an important role in energy production, metabolic regulation, and acid-base balance, among other things.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate is chemically stable and is a positively charged molecule. It has the ability to redox reactions in living organisms and is involved in many important redox processes.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate is mainly used for many redox reactions in cells. It plays the role of a hydrogen carrier in processes such as cellular respiration, photosynthesis and fatty acid synthesis, and participates in energy conversion. It is also involved in antioxidant reactions and cellular DNA repair processes.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate is mainly prepared by chemical synthesis or extraction from living organisms. The chemical synthesis method is mainly formed by the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine mononucleotide and phosphorylation, and then the double nucleotide structure is formed through ligation reaction. Methods of extraction from organisms can be obtained by enzymatic methods or other isolation techniques.
When using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, there is a certain amount of safety that needs to be followed. It is chemically non-toxic to humans, but it may cause gastrointestinal upset if ingested in excess. It is relatively unstable in a humid environment and decomposes easily. Pay attention to storage and avoid exposure to acidic or alkaline environments.