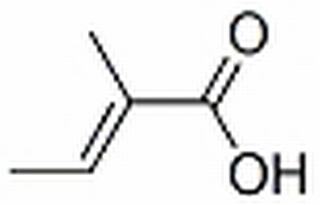
trans-2,3-Dimethylacrylic acid CAS 80-59-1
| Hazard Symbols | Xi – Irritant |
| Risk Codes | R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| UN IDs | UN 3261 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | GQ5430000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29161980 |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| Packing Group | III |
trans-2,3-Dimethylacrylic acid CAS 80-59-1
quality
Trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid is a colorless liquid. It is acidic and can react with bases to form the corresponding salts. It can react violently with oxygen at room temperature and may spontaneously combust. It can also react with some metals to form the corresponding metal salts. Trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid has good solubility and can be dissolved in water and organic solvents. In industry, it is often used as an intermediate in the synthesis of organic compounds, and can also be used in the preparation of certain polymers, plastics, and coatings.
Uses and synthesis methods
Trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid, also known as methylisobutenic acid, is an unsaturated carboxylic acid containing two methyl groups. It has a wide range of applications.
Trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid is used as a monomer in the synthesis of polymers. It can be copolymerized with other monomers through free radical polymerization reaction, such as copolymerization with acrylic acid and methyl acrylate to obtain methylisopropyl methyl acrylate copolymer. These polymers have good properties in paints, coatings, adhesives, etc., and are used to increase the impact resistance of products, reduce viscosity, etc.
Secondly, trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid can also be used as an important intermediate in synthetic organic synthesis. Its two methyl groups provide the active site for the reaction, and a variety of organic substances can be prepared by further functional group conversion reactions. For example, by reacting it with amines or alcohols, biologically active compounds, such as plant growth regulators, can be synthesized.
The synthesis method of trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid is commonly prepared by the reaction of isobutylene with carbon monoic acid hydrate. Isobutylene is reacted with peracid positive iron to obtain the substrate methylisobutenic acid, which is then reacted with excess cuprous chloride to form internal salts, and then reacted with alcohol to hydrolyze to form the corresponding acrylic acid.
Safety Information
Trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid is a common organic compound, and its safety information is as follows:
1. Toxicity: trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid has certain toxicity and may cause irritation and damage to the human body. When using or handling this compound, appropriate precautions must be taken to avoid direct contact with the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.
2. Fire hazard: Trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid is a flammable substance that produces combustible vapors at high temperatures. When handling or storing this compound, avoid ignition and high temperatures, and maintain good ventilation.
3. Storage requirements: trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid should be stored in an airtight container, away from fire sources and oxidants. It should be stored in isolation from combustibles, oxidants, and strong acids to avoid accidental reactions.
4. Emergency response: In the event of a spill or accident, necessary emergency measures should be taken immediately, such as wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, evacuating people quickly, and preventing substances from entering sewers or underground water sources.
5. Exposure prevention: When handling trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid, personal protective equipment such as protective gloves, goggles, and protective clothing should be worn to ensure the safety of the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.
6. Waste disposal: Waste trans-2,3-dimethacrylic acid should be properly disposed of in accordance with local regulations. Avoid dumping waste into the natural environment and hand it over to a specialized waste treatment facility for disposal.