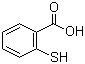
Thiosalicylic acid(CAS#147-93-3)
| Hazard Symbols | Xn – Harmful |
| Risk Codes | R20/21/22 – Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. |
Thiosalicylic acid(CAS#147-93-3) Introduction
quality
O-carboxyphenylthiophenol is an organic compound. It is a yellowish crystalline or powdery solid.
O-carboxyphenylthiophenol has the characteristic combination of phenol and thiophenol, and has strong physicochemical properties. Here are some of its main properties:
1. Solubility: o-carboxyphenylthiophenol is slightly soluble in water and soluble in organic solvents such as ethers, alcohols and ketones.
2. Acidic: o-carboxyphenylthiophenol is a weak acid, and its hydroxyl group can react with bases to form corresponding salts.
3. Oxidation: O-carboxyphenylthiophenol has a certain oxidation and can be oxidized by many strong oxidants (such as hydrogen peroxide).
4. Reducibility: Under appropriate conditions, o-carboxyphenylthiophenol can undergo a reduction reaction to reduce to the corresponding phenol or thiophenol.
O-carboxyphenylthiophenol has a wide range of application fields and is mainly used as a raw material for reagents and catalysts in organic synthesis reactions. It is also widely used in dyes, fluorescents, rubber plasticizers, and other fields. It has antioxidant, antiseptic and other properties, and can also be used as a preservative and antioxidant. Safety Information
O-carboxyphenthiophenol is an organic compound, also known as o-carboxyphenylthiophenolic acid or 2-hydroxy-5-carboxythiophenol. The safety information about it is as follows:
1. Toxicity: O-carboxyphenylthiophenol has certain toxicity and should be avoided in contact with the skin, eyes and respiratory tract.
2. Burns: O-carboxyphenylthiophenol is an irritating substance that may cause skin and eye burns.
3. Inhalation: Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of o-carboxyphenylthiophenol vapor may cause respiratory irritation. It should be operated in a well-ventilated area with appropriate protective equipment.
4. Storage: O-carboxyphenylthiophenol should be stored in a dry, cool, well-ventilated place, away from ignition sources and oxidants, to prevent the risk of fire and explosion.
5. Packaging: During transportation and storage, containers and packaging materials that meet safety standards should be used.
6. Waste disposal: In accordance with local laws and regulations, the waste o-carboxyphenylthiophenol is disposed of safely. Avoid direct discharge into water bodies or the environment to avoid pollution to the environment.
During use, please strictly follow the safety operation procedures and ensure that you have the necessary protective equipment and emergency measures. Uses and synthesis methods
O-carboxyphenylthiophenol is an organic compound. It is a derivative of o-hydroxythiophenol.
O-carboxyphenthiophenol is often used as a fungicide and preservative. O-carboxyphenylthiophenol is also used in the wood, paper and dye industries.
The synthesis methods of o-carboxyphenylthiophenol are generally as follows:
Carboxylation: Phenylthiophenol is reacted with bromoacetic acid or acid chloride to form o-carboxyphenylthiophenol.
Hydroxylation reaction: o-hydroxyphenylthionol is reacted with carboxylic acid to form o-carboxyphenthionol.
Acylation reaction: o-hydroxyphenylthionol is reacted with anhydride to produce o-carboxyphenylthionol.
Each of these methods is highly efficient in the synthesis of o-carboxyphenylthiophenol, depending on the experimental conditions and the desired yield.