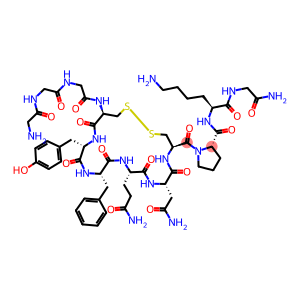
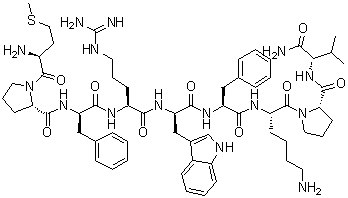
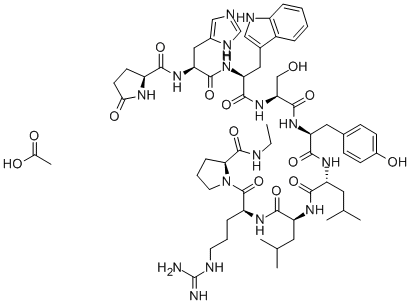
Terlipressin(CAS#14636-12-5)
Terlipressin,CAS14636-12-5,pharmachologic effect
Terlipressin is a synthetic vasopressin analogue. It can selectively act on the V1 receptor of vascular smooth muscle, causing splanchnic vasoconstriction, thereby reducing the blood flow of internal organs, especially the portal system, reducing portal pressure, and effectively controlling esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding.
It also has the effect of reducing hepatic venous wedge pressure and reducing asympathetic venous blood flow, which is of great significance in improving the symptoms related to portal hypertension.
In some cases, it can also be used to treat hypotension caused by other causes, by constricting blood vessels to raise blood pressure and maintain blood perfusion to vital organs.
Clinical application
Main application: It is mainly used for the treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding, which can quickly and effectively control bleeding, improve the survival rate of patients, and buy time for subsequent further treatment. For example, during acute bleeding, intravenous terlipressin can quickly reduce the pressure of varicose veins and achieve hemostasis.
Other applications: It can also be used to treat hepatorenal syndrome, improve blood perfusion of the kidneys, increase glomerular filtration rate, and help improve renal function. In hypotensive states caused by septic shock, terlipressin can be used as an adjunctive therapy to raise blood pressure if conventional fluid resuscitation and other treatments are inadequate.
Adverse effects
Common adverse reactions: It may cause symptoms such as paleness, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, etc. These adverse effects are usually related to drug-induced vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal smooth muscle contraction.
Serious adverse reactions: In some patients, serious adverse reactions of the cardiovascular system such as myocardial ischemia and arrhythmias may occur, especially if the dose is too large or the patient has serious cardiovascular disease. It may also lead to acral ischemia, local tissue necrosis, etc., and it is necessary to pay close attention to the reaction after medication.