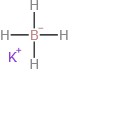
Potassium borohydride(CAS#13762-51-1)
| Risk Codes | R14/15 - R24/25 - R34 – Causes burns R11 – Highly Flammable |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S43 – In case of fire use … (there follows the type of fire-fighting equipment to be used.) S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S7/8 - S28A - S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. |
| UN IDs | UN 1870 4.3/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | - |
| RTECS | TS7525000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 10 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 2850 00 20 |
| Hazard Class | 4.3 |
| Packing Group | I |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 167 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit 230 mg/kg |
Introduction
Potassium borohydride is an inorganic compound. Its properties are as follows:
1. Appearance: Potassium borohydride is a white crystalline powder or granule.
3. Solubility: Potassium borohydride is soluble in water and gradually hydrolyzed in water to produce hydrogen and potassium hydroxide.
4. Specific gravity: The density of potassium borohydride is about 1.1 g/cm³.
5. Stability: Under normal conditions, potassium borohydride is relatively stable, but it may decompose in the presence of high temperature, high humidity and strong oxidants.
The main uses of potassium borohydride include:
1. Hydrogen source: Potassium borohydride can be used as a reagent for the synthesis of hydrogen, which is produced by reacting with water.
2. Chemical reducing agent: potassium borohydride can reduce a variety of compounds to corresponding organic compounds such as alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones.
3. Metal surface treatment: Potassium borohydride can be used for electrolytic hydrogenation treatment of metal surfaces to reduce surface oxides.
The preparation methods of potassium borohydride mainly include direct reduction method, antiborate method and aluminum powder reduction method. Among them, the most commonly used method is obtained by the reaction of sodium phenylborate and hydrogen under the action of a catalyst.
The safety information of potassium borohydride is as follows:
1. Potassium borohydride has strong reducibility, and hydrogen is produced when it reacts with water and acid, so it needs to be operated in a well-ventilated place.
2. Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and respiratory tract to prevent irritation and injury.
3. When storing and using potassium borohydride, care should be taken to prevent contact with oxidants and other substances to prevent fire or explosion.
4. Do not mix potassium borohydride with acidic substances to avoid the formation of dangerous gases.
5. When disposing of potassium borohydride waste, the relevant environmental and safety regulations should be followed.