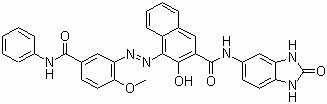
Pigment Red 176 CAS 12225-06-8
Pigment Red 176 CAS 12225-06-8
quality
Pigment Red 176, also known as bromoanthraquinone red, is an organic pigment. Its chemical structure contains anthraquinone groups and bromine atoms. Here are some of its properties:
1. Color stability: Pigment Red 176 has good color stability, is not easily affected by light, heat, oxygen or chemicals, and can maintain a bright red color for a long time in outdoor environments.
2. Lightfastness: Pigment Red 176 has good lightfastness to ultraviolet rays and is not easy to fade or fade. It is commonly used for coloring materials such as outdoor paints, plastics, and textiles.
3. Heat resistance: Pigment Red 176 can also maintain a certain stability at high temperatures, and has a wide range of applications in thermoplastic materials.
4. Chemical resistance: Pigment Red 176 has a certain resistance to general solvents and chemicals, and is not easy to be corroded or discolored by chemicals such as acids and alkalis.
5. Solubility: Pigment Red 176 has a certain solubility in some organic solvents, and can be easily mixed with other pigments to blend a variety of colors.
Uses and synthesis methods
Pigment Red 176, also known as ferrite red, is a widely used pigment. Its main uses are as follows:
1. Printing industry: Pigment Red 176 can be used as an ink pigment in printing and dye preparation. It has a vivid color and good fade stability.
2. Coating industry: Pigment Red 176 can be used to prepare coatings, such as water-based coatings, solvent-based coatings and stucco coatings. It is able to provide a brilliant red color to the coating.
3. Plastic products: Pigment Red 176 has heat resistance, weather resistance and good durability, it can be used to make plastic products, such as plastic toys, pipes, car parts, etc.
4. Ceramic industry: Pigment red 176 can be applied to ceramic products, such as ceramic tiles, ceramic tableware, etc. It can provide a rich red hue.
A common method for the synthesis of pigment red 176 is prepared by high-temperature solid-phase reaction. The specific steps are as follows:
1. Add an appropriate amount of iron(III.) chloride and an appropriate amount of oxidant (such as hydrogen peroxide) to the reaction flask.
2. After the reaction bottle is sealed, it is placed in a high-temperature furnace for high-temperature solid-state reaction. The reaction temperature is usually between 700-1000 degrees Celsius.
3. After a certain period of reaction, take out the reaction bottle and cool it to obtain pigment red 176.