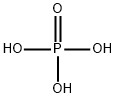
Phosphoric acid CAS 7664-38-2
| Hazard Symbols | C – Corrosive |
| Risk Codes | R34 – Causes burns |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) |
| UN IDs | UN 1805 |
Introduction
Phosphoric acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It appears as colorless, transparent crystals and is easily soluble in water. Phosphoric acid is acidic and can react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, as well as react with alcohols to form phosphate esters.
Phosphoric acid is widely used in various industries, including as a raw material for the production of fertilizers, cleaning agents, and food additives. It is also used in the manufacture of phosphate salts, pharmaceuticals, and in chemical processes. In biochemistry, phosphoric acid is an important component of cells, participating in energy metabolism and DNA synthesis, among other biological processes.
The production of phosphoric acid typically involves wet and dry processes. The wet process involves heating phosphate rock (such as apatite or phosphorite) with sulfuric acid to produce phosphoric acid, while the dry process involves the calcination of phosphate rock followed by wet extraction and reaction with sulfuric acid.
In industrial production and use, phosphoric acid poses certain safety risks. Highly concentrated phosphoric acid is strongly corrosive and can cause irritation and damage to the skin and respiratory tract. Therefore, proper protective measures should be taken to avoid skin contact and inhalation of its vapors when handling phosphoric acid. Moreover, phosphoric acid also poses environmental risks, as excessive discharge can lead to water and soil pollution. Hence, strict control and proper waste disposal practices are essential during production and use.