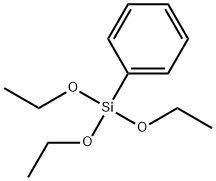
Phenyltriethoxysilane; PTES(CAS#780-69-8)
| Risk Codes | R10 – Flammable R21 – Harmful in contact with skin R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S37/39 – Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| UN IDs | UN 1993 3/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VV4900000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 10-21 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29310095 |
| Hazard Class | 3.2 |
| Packing Group | III |
Introduction
Phenyltriethoxysilane. The following is an introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of phenytriethoxysilanes:
Quality:
1. The appearance is colorless or yellowish liquid.
2. It has a low vapor pressure and a high flash point at room temperature.
3. Insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents such as ether, chloroform and alcohol solvents.
4. It has good chemical stability and can withstand higher temperature and oxidation environment.
Use:
1. As a chemical reagent for organic synthesis, it can be used to synthesize other organosilicon compounds.
2. As a surfactant and dispersant, it can be used in industrial applications such as coatings, wallpaper and inks.
3. In the field of electronics, it can be used to prepare silicone materials, such as optical fiber coating and electronic packaging materials.
Method:
A commonly used preparation method is to react phenyltrimethylsilane with ethanol under alkaline conditions to obtain phenyl triethoxysilane.
Safety Information:
1. Phenyltriethoxysilane is a flammable liquid and should be kept away from open flames and ignition sources.
2. Avoid skin contact and inhalation, and wear protective gloves, protective glasses and respiratory protective equipment when necessary.
3. In case of accidental contact or inhalation, rinse immediately with plenty of water or seek medical assistance.
4. When storing, it should be sealed and stored, away from sunlight and heat sources, and not mixed with oxidants.