Oxytocin(CAS#50-56-6)
| Hazard Symbols | Xi – Irritant |
| Risk Codes | 36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36 – Wear suitable protective clothing. |
| UN IDs | 3249 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RS7534000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 3-8-10-23 |
| HS Code | 2937190000 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in rat: > 20520ug/kg |
Introduction
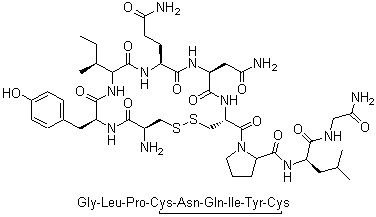
Oxytocin is a hormone released by the posterior pituitary gland of the human body and its main role is to promote the progress of uterine contractions and labor. The chemical name of oxytocin is oxytocin-8, and it is a polypeptide composed of nine amino acid residues. The main use of oxytocin is in obstetrics and gynecology medicine to facilitate the process of childbirth. It can induce contractions by increasing the strength and frequency of contractions in the smooth muscles of the uterus and shorten the duration of labor. In some cases, such as abnormal fetal monitoring or slow labor, oxytocin may be used to stimulate contractions to maintain and improve fetal health. There are two common ways to prepare oxytocin. One is extracted from the pituitary gland of the back of the human brain and obtained pure oxytocin after a high degree of purification and preparation. Another method is to use the technique of chemical synthesis to synthesize nine amino acid residues into polypeptide chains in a specific order. The use of oxytocin requires strict medical supervision and dosage control to avoid possible side effects. Common side effects include uterine contractions that are too strong, uterine rupture, fetal distress, intrauterine infection, etc. Oxytocin should only be used correctly under the guidance of a clinician, while the patient’s response and fetal condition need to be closely monitored. The use of oxytocin is also limited by some contraindications, such as uterine scarring, placental abruption, placenta previa, etc. Before oxytocin is used, the physician should conduct a thorough evaluation of the patient and decide whether to use the appropriate dose and method of oxytocin based on the patient’s specific situation.