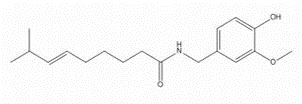
Nonivamide(CAS# 404-86-4)
| Risk Codes | R25 – Toxic if swallowed R37/38 – Irritating to respiratory system and skin. R41 – Risk of serious damage to eyes R42/43 – May cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact. R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S22 – Do not breathe dust. S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S28 – After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of soap-suds. S36/39 - S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. |
| UN IDs | UN 2811 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | RA8530000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 10-21 |
| HS Code | 29399990 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in mouse: 47200ug/kg |
Introduction
Capsaicin, also known as capsaicin or capsaithin, is a compound found naturally in chili peppers. It is a colorless crystal with a special spicy taste and is the main spicy component of chili peppers.
Properties of capsaicin include:
Physiological activity: Capsaicin has a variety of physiological activities, which can promote the secretion of digestive juices, increase appetite, eliminate fatigue, improve cardiovascular health, etc.
High-temperature stability: Capsaicin does not break down easily at high temperatures, maintaining its spiciness and color during cooking.
The main preparation methods of capsaicin are as follows:
Natural extraction: Capsaicin can be extracted by crushing the pepper and using a solvent.
Synthesis and preparation: Capsaicin can be synthesized by chemical reaction, and the commonly used methods include sodium sulfite method, sodium o-sulfate method and heterogeneous catalytic method.
Excessive intake of capsaicin may lead to adverse effects such as indigestion, gastrointestinal irritation, etc. Sensitive people such as gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, etc. should be used with caution.
Capsaicin can cause eye and skin irritation, so care should be taken to avoid contact with eyes and sensitive skin.