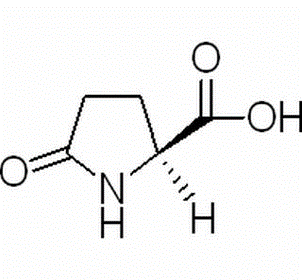
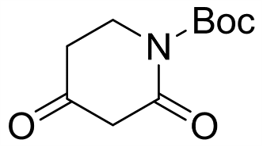
L-Pyroglutamic acid CAS 98-79-3
Risk and Safety
| Hazard Symbols | Xi – Irritant |
| Risk Codes | 36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36 – Wear suitable protective clothing. S37/39 – Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | TW3710000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 21 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29337900 |
| Introduction | pyroglutamic acid is 5-oxyproline. It is formed by dehydration between α-NH2 group and γ-hydroxyl group of glutamic acid to form a molecular lactam bond; It can also be formed by losing an Amido group in a glutamine molecule. If glutathione synthetase deficiency, can cause pyroglutamemia, a series of clinical symptoms. Pyroglutamemia is a disorder of organic acid metabolism caused by glutathione synthetase deficiency. Clinical manifestations of birth 12~24 hours of onset, progressive hemolysis, jaundice, chronic Metabolic Acidosis, mental disorders, etc.; Urine contains pyroglutamic acid, lactic acid, Alpha deoxy4 glycoloacetic acid lipid. Treatment, symptomatic, pay attention to adjust the diet after age. |
| properties | L-pyroglutamic acid, also known as L-pyroglutamic acid, L-pyroglutamic acid. From the ethanol and petroleum ether mixture in the precipitation of colorless orthorhombic double cone Crystal, melting point of 162~163 ℃. Soluble in water, alcohol, acetone and acetic acid, ethyl acetate-soluble, insoluble in ether. Specific optical rotation -11.9 °(c = 2,H2O). |
| Features and uses | in human skin contains a moisturizing function of water-soluble substances-natural moisturizing factor, its composition is roughly amino acid (containing 40%), pyroglutamic acid (containing 12%), inorganic salts (Na, K, Ca, Mg, etc. containing 18.5%), and other organic compounds (containing 29.5%). Therefore, pyroglutamic acid is one of the main components of skin natural moisturizing factor, and its moisturizing ability far exceeds that of glycerol and propylene glycol. And non-toxic, no stimulation, is a modern Skin Care, Hair Care cosmetics excellent raw materials. Pyroglutamic acid also has an inhibitory effect on the activity of tyrosine oxidase, thereby preventing the deposition of “melanoid” substances in the skin, which has a whitening effect on the skin. Has a softening effect on the skin, can be used for nail cosmetics. In addition to the application in cosmetics, L-pyroglutamic acid can also produce derivatives with other organic compounds, which have special effects on surface activity, transparent and bright effect, etc. It can also be used as a surfactant for detergents; Chemical reagents for the resolution of racemic amines; Organic intermediates. |
| preparation method | L-pyroglutamic acid is formed by removing one minute of water from the molecule of L-glutamic acid, and its preparation process is simple, the key steps are the control of temperature and dewatering time. (1) 500g of L-glutamic acid was added to a 100 ml beaker, and the beaker was heated with an oil bath, and the temperature was raised to 145 to 150 ° C., and the temperature was maintained for 45 minutes for dehydration reaction. The dehydrated solution was Tan. (2) after completion of the dehydration reaction, the solution was poured into boiling water with a volume of about 350, and the solution was completely dissolved in water. After cooling to 40 to 50 ° C., an appropriate amount of activated carbon was added for decoloration (repeated twice). A colorless transparent solution was obtained. (3) when the colorless transparent solution prepared in step (2) is directly heated and evaporated to reduce the volume to about half, turn to the water bath and continue to concentrate to a volume of about 1/3, you can stop heating, and in the hot water bath to slow the crystallization, 10 to 20 hours after the preparation of colorless prismatic crystals. The amount of L-pyroglutamic acid in cosmetics depends on the formulation. This product can also be used on cosmetics in the form of 50% concentrated solution. |
| glutamic acid | glutamic acid is an amino acid constituting a protein, has an ionized acidic side chain, and exhibits hydrotropism. Glutamic acid is susceptible to cyclization into pyrrolidone carboxylic acid, I .e., pyroglutamic acid. glutamic acid is particularly high in all cereal proteins, providing alpha-ketoglutarate through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Alpha ketoglutaric acid can be directly synthesized from ammonia under the catalysis of glutamate dehydrogenase and NADPH (coenzyme II), and can also be catalyzed by aspartate aminotransferase or alanine aminotransferase, glutamic acid is produced by transamination of aspartic acid or alanine; In addition, glutamic acid can be reversibly transformed with proline and ornithine (from arginine), respectively. Glutamate is therefore a nutritionally non-essential amino acid. When glutamic acid is deaminated under the catalysis of glutamate dehydrogenase and NAD (coenzyme I) or is transferred out of the amino group under the catalysis of aspartate aminotransferase or alanine aminotransferase to produce alpha ketoglutarate, it enters the tricarboxylic acid cycle and generates sugars through the gluconeogenic pathway, so glutamic acid is an important glycogenic amino acid. glutamic acid in different tissues (such as muscle, liver, brain, etc.) can synthesize glutamine with NH3 through the catalysis of glutamine synthetase, it is the detoxification product of ammonia, especially in brain tissue, and also the storage and utilization form of ammonia in the body (see “glutamine and its metabolism”). glutamic acid is synthesized with acetyl-CoA as a cofactor of mitochondrial carbamoyl phosphate synthase (involved in the synthesis of urea) through the catalysis of acetyl-glutamate synthase. γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a product of the decarboxylation of glutamic acid, especially in high concentrations in brain tissue, and also appears in the blood, its physiological function is considered to be inhibitory neurotransmitter, the antispasmodic and hypnotic effects exerted by the clinical infusion of echinocandin may be achieved through GABA. The catabolism of GABA enters the tricarboxylic acid cycle by converting GABA transaminase and aldehyde dehydrogenase into succinic acid to form a GABA shunt. |
| Use | used as intermediates in organic synthesis, food additives, etc. used in food, medicine, cosmetics and other industries |
Write your message here and send it to us