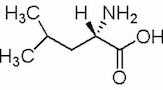
L-Leucine CAS 61-90-5
| Safety Description | 24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OH2850000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29224995 |
Introduction
L-leucine is an amino acid that is one of the building blocks of proteins. It is a colorless, crystalline solid that is soluble in water.
There are two main methods for the preparation of L-leucine: natural method and chemical synthesis method. Natural methods are often synthesized by the fermentation process of microorganisms, such as bacteria. The chemical synthesis method is prepared through a series of organic synthesis reactions.
Safety Information of L-Leucine: L-Leucine is relatively safe in general. Excessive intake may cause gastrointestinal upset, diarrhea, and other symptoms. For people with renal insufficiency or metabolic abnormalities, care should be taken to avoid excessive intake.
Write your message here and send it to us