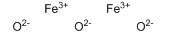Iron(III) oxide CAS 1309-37-1
| Hazard Symbols | Xi – Irritant |
| Risk Codes | R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. |
| UN IDs | UN 1376 |
Iron(III) oxide CAS 1309-37-1 introduce
quality
Orange-red to purplish-red trigonal crystalline powder. Relative density 5. 24。 Melting point 1565 °C (decomposition). Insoluble in water, soluble in hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, slightly soluble in nitric acid and alcohol. When burned, oxygen is released, which can be reduced to iron by hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Good dispersion, strong tinting and hiding power. No oil permeability and no water permeability. Temperature-resistant, light-resistant, acid-resistant and alkali-resistant.
Method
There are wet and dry preparation methods. Wet products have fine crystals, soft particles, and are easy to grind, so they are suitable for pigments. Dry products have large crystals and hard particles, and are suitable for magnetic materials and polishing and grinding materials.
Wet method: a certain amount of 5% ferrous sulfate solution is quickly reacted with an excess caustic soda solution (an excess alkali of 0.04~0.08g/mL is required), and the air is introduced at room temperature to make it all turn into a reddish-brown iron hydroxide colloidal solution, which is used as the crystal nucleus for depositing iron oxide. With the above-mentioned crystal nucleus as the carrier, with ferrous sulfate as the medium, the air is introduced, at 75~85 °C, under the condition of the presence of metallic iron, the ferrous sulfate reacts with the oxygen in the air to generate ferric oxide (i.e., iron red) deposited on the crystal nucleus, and the sulfate in the solution reacts with the metallic iron to regenerate ferrous sulfate, and the ferrous sulfate is oxidized into iron red by the air and continues to be deposited, so that the cycle ends at the end of the whole process to generate iron oxide red.
Dry method: nitric acid reacts with iron sheets to form ferrous nitrate, which is cooled and crystallized, dehydrated and dried, and calcined at 600~700 °C for 8~10h after grinding, and then washed, dried and crushed to obtain iron oxide red products. Iron oxide yellow can also be used as raw material, and iron oxide red can be obtained by calcination at 600~700 °C.
use
It is an inorganic pigment and is used as an anti-rust pigment in the coating industry. It is also used as a colorant for rubber, artificial marble, terrazzo on the ground, colorants and fillers for plastics, asbestos, artificial leather, leather polishing paste, etc., polishing agent for precision instruments and optical glass, and raw materials for the manufacture of magnetic ferrite components.
security
Packed in woven bags lined with polyethylene plastic bags, or packed in 3-layer kraft paper bags, with a net weight of 25kg per bag. It should be stored in a dry place, do not get damp, avoid high temperature, and should be isolated from acid and alkali. The effective storage period of the unopened package is 3 years. Toxicity and protection: Dust causes pneumoconiosis. The maximum allowable concentration in the air, iron oxide aerosol (soot) is 5mg/m3. Pay attention to dust.