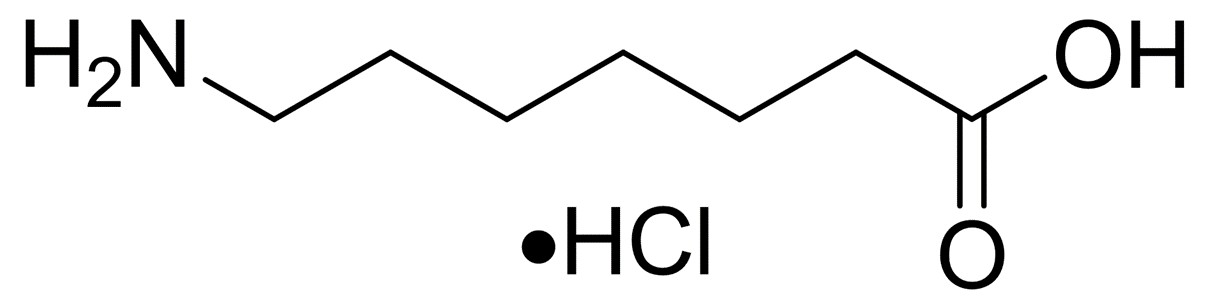
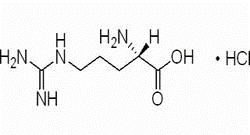
Heptanoic acid,7-amino-, hydrochloride (1:1)(CAS#62643-56-5)
Heptanoic acid,7-amino-, hydrochloride (1:1)(CAS#62643-56-5)
Heptanoic acid,7-amino-, hydrochloride (1:1), CAS number 62643-56-5, has non-negligible properties and application potential in the fields of chemistry and biomedicine.
In terms of chemical structure, it is a compound formed by the salt of 7-aminoheptanoic acid and hydrochloric acid in a ratio of 1:1. The amino group in the molecule gives it a certain alkalinity, which can be combined with hydrochloric acid to form a stable salt structure, which not only changes the physical properties of the original substance, such as solubility, melting point, etc., but also makes it more stable during storage and use. The long-chain heptanoic acid structure brings hydrophobicity to the molecule, which contrasts with the hydrophilicity of the amino group and constructs a unique amphiphilic characteristic. Usually presented as a white crystalline powder, this solid form facilitates the processing and molding of pharmaceutical preparations, and is conducive to making tablets, capsules and other dosage forms. In terms of solubility, it has good solubility due to salt formation in water, which is greatly improved compared with free 7-aminoheptanoic acid, and can also show moderate solubility in some polar organic solvents, which provides convenience for subsequent chemical reactions and drug synthesis.
In biomedical applications, it shows great potential. As an amino acid derivative, it may be involved in human metabolic processes or as a precursor to the synthesis of biologically active molecules. In the field of drug research and development, its structure is similar to some known neurotransmitters or bioactive substances, and it is promising that through further modification and modification, new drugs for neurological diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, etc., can be developed to exert therapeutic effects by regulating nerve signaling pathways and supplementing neurotransmitters. In addition, in the field of tissue engineering, based on its unique amphiphilia and biocompatibility, it is expected to be used to construct biomimetic materials to promote cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation, and help the repair and regeneration of tissues and organs.
In terms of preparation method, 7-aminoheptanoic acid is generally prepared by organic synthesis, and then hydrochloric acid is introduced into salt by acid-base neutralization reaction. The process of synthesizing 7-aminoheptanoic acid involves a multi-step organic reaction, starting from simple raw materials such as fatty acids and amines, and going through steps such as amidation and reduction.