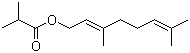
Geranyl isobutyrate(CAS#2345-26-8)
| Toxicity | Both the acute oral LD50 value in rats and the acute dermal LD50 value in rabbits exceeded 5 g/kg (Shelanski, 1973). |
Introduction
Geranyl isobutyrate is an organic compound. The following is an introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of geranyl isobutyrate:
Quality:
Appearance and smell: Geranyl isobutyrate is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with tangerine and grapefruit-like aromas.
Density: The density of geraniate isobutyrate is about 0.899 g/cm³.
Solubility: geraniate isobutyrate is soluble in ethanol and ether, insoluble in water.
Use:
Chemical synthesis intermediates: geranyl isobutyrate can also be used as an important intermediate in the synthesis of other organic compounds.
Method:
Geranyl isobutyrate is usually obtained by the reaction of isobutanol with geranitol. The reaction is usually carried out in the presence of an acidic catalyst, such as sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid.
Safety Information:
Fire hazard: geranyl isobutyrate is a flammable liquid that is prone to fire when heated, and should be kept away from open flames and high temperatures.
Storage Caution: Geranyl isobutyrate should be stored in an airtight container to prevent contact with air.
Contact caution: Exposure to geranyl isobutyrate may cause skin irritation and eye irritation, and precautions should be taken such as wearing gloves and goggles.
Toxicity: Based on available studies, geranyl isobutyrate does not have significant toxicity at presumed dosages, but prolonged exposure or ingestion of larger doses should still be avoided.
Before using geranyl isobutyrate, it is important to have a detailed understanding of the relevant protocols, safe practices, and regulatory requirements.