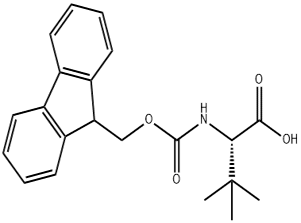
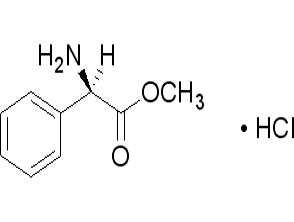
Fmoc-L-tert-leucine (CAS# 132684-60-7)
Risk and Safety
| Safety Description | S22 – Do not breathe dust. S24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29242990 |
| Hazard Class | IRRITANT |
Introduction:
Introducing Fmoc-L-tert-leucine (CAS# 132684-60-7), a premium amino acid derivative that is essential for peptide synthesis and research applications. This high-purity compound is designed for chemists and researchers who demand precision and reliability in their work. Fmoc-L-tert-leucine is a protected form of the amino acid leucine, featuring a 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) group that allows for selective deprotection during peptide synthesis, making it an invaluable tool in the field of organic chemistry.
With its unique structure, Fmoc-L-tert-leucine offers enhanced stability and solubility, ensuring optimal performance in various chemical reactions. This compound is particularly useful in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), where the Fmoc protection group can be easily removed under mild basic conditions, facilitating the sequential addition of amino acids to build complex peptide chains. Its tert-butyl side chain provides steric hindrance, which can be advantageous in controlling the conformation of peptides, ultimately influencing their biological activity.
Our Fmoc-L-tert-leucine is manufactured under stringent quality control measures, ensuring that it meets the highest standards for purity and consistency. It is available in various quantities to suit your specific research needs, whether you are working on small-scale projects or large-scale peptide synthesis.
In addition to its applications in peptide synthesis, Fmoc-L-tert-leucine is also a valuable reagent in the development of pharmaceuticals, bioconjugates, and other bioactive compounds. Its versatility and reliability make it a must-have for any laboratory focused on peptide chemistry.
Elevate your research and synthesis capabilities with Fmoc-L-tert-leucine (CAS# 132684-60-7) – the ideal choice for chemists seeking quality and performance in their peptide synthesis endeavors.