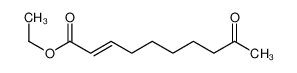
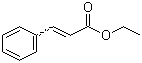
ethyl 9-oxodec-2-enoate(CAS#57221-88-2)
ethyl 9-oxodec-2-enoate(CAS#57221-88-2) Introduction
Physical:
Appearance: Usually colorless to light yellow liquid with a peculiar odor.
Boiling point: Generally around [specific boiling point value] °C (at standard atmospheric pressure), its boiling point characteristics determine the temperature conditions in separation and purification operations such as distillation, which is of great significance for separating the compound from the reaction mixture.
Density: The relative density is about [specific density value] (water = 1), which helps to determine the stratification of it when it is mixed with other substances and the distribution state in the reaction system during storage and use.
Solubility: It has good solubility in common organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, chloroform, etc., and can be miscible with these organic solvents, which is convenient for participating in various reactions as reactants or intermediates in organic synthesis reactions, while the solubility in water is relatively poor.
Chemical properties:
Functional group reactivity: The molecule contains ester groups and alkene bonds, two important functional groups, which make it rich in chemical reactivity. Ester groups can undergo hydrolysis reactions to generate corresponding alcohols and acids under acidic or alkaline conditions, and this reaction is often used in functional group conversion and compound modification in organic synthesis. Olefin bonds can participate in addition reactions, such as hydrogenation reactions with hydrogen to saturate double bonds; It can also undergo electrophilic addition reactions with halogens, hydrogen halides, etc., so as to introduce new functional groups and construct more complex organic molecular structures for the synthesis of compounds with specific functions.
Stability: It is relatively stable at room temperature and pressure, but its molecular structure may change under conditions such as light, high temperature, strong oxidant or strong acid and alkali. For example, alkene bonds may undergo free radical reactions under light or high temperatures, resulting in migration or oxidation of double bonds; The ester group accelerates the hydrolysis reaction under strong acid-base conditions, which changes the chemical properties and reactivity of the compound. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to avoid contact with these adverse conditions during storage and use, and it is generally suitable for storage in a cool, dry, dark and away environment away from strong oxidants and acids and alkalis.