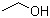Ethanol(CAS#64-17-5)
| Hazard Symbols | F – Flammable |
| Risk Codes | R11 – Highly Flammable |
| Safety Description | S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S7 – Keep container tightly closed. |
| UN IDs | UN 1170/1986/1987 |
Ethanol(CAS#64-17-5)
Physical
Appearance: Colorless transparent liquid.
Smell: It has a special aroma and is slightly pungent, with the smell of wine and a pungent spicy taste.
Density: 0.789g/cm³ (liquid)
Melting Point: -114°C
Boiling Point: 78.4 °C
Solubility: miscible with water, miscible in methanol, ether, chloroform and other organic solvents.
Flash Point: 12.78°C
Chemical properties
Oxidation reaction: light blue flame is emitted when burned, carbon dioxide and water are generated; Under the action of oxidants such as potassium permanganate or potassium dichromate, it can be rapidly oxidized to form acetaldehyde, which is further oxidized to form acetic acid.
Reduction reaction: It can react with alkali metals to release hydrogen, such as sodium ethanol and hydrogen gas by reacting with sodium metal.
Dehydration reaction: mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid for coheating, intramolecular dehydration at about 170 °C to form ethylene; At around 140°C, intermolecular dehydration is used to form ether.
Esterification reaction: reacts with organic acids to form esters, and this reaction is reversible.
Dehydrogenation: When ethanol vapor is used at 200°C-300°C and copper is used as a catalyst, acetaldehyde is obtained by one-step dehydrogenation.
Halogenation: In reaction with hydrohalic acid, the hydroxyl group is replaced by a halogen to form halocarbons and water.
Preparation method:
Fermentation method
Grain fermentation method: starch-rich cereals, potatoes and other agricultural products are washed and crushed and then cooked under pressure to make starch gelatinized, amylase is added to hydrolyze into maltose and glucose, and then yeast is added to ferment to obtain ethanol.
Wood hydrolysis fermentation method: hydrolyze wood with sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, turn fiber into glucose, and then enter the fermentation stage to produce ethanol.
Ethanol production method from sulfite waste lye: the waste sulfite alkali solution of fiber and paper enterprises is processed, and the cellulose in it is converted into glucose, and ethanol is obtained after fermentation.
Ethylene hydration
Indirect hydration: Also known as sulfuric acid method, ethylene and sulfuric acid react to produce ethyl bisulfate or diethyl sulfate, and then the sulfate is hydrolyzed to obtain ethanol.
Direct hydration: Ethylene and water are directly added under catalyst, high temperature, and pressure conditions to obtain ethanol.