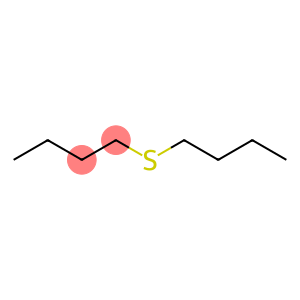
Dibutyl sulfide(CAS#544-40-1)
| Hazard Symbols | Xi – Irritant |
| Risk Codes | R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. R41 – Risk of serious damage to eyes |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S36 – Wear suitable protective clothing. |
| UN IDs | 2810 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | ER6417000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 13 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29309070 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| Packing Group | III |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 2220 mg/kg |
Introduction
Dibutyl sulfide (also known as dibutyl sulfide) is an organic compound. The following is an introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of dibutyl sulfide:
Quality:
- Appearance: BTH is usually a colorless liquid with a peculiar thioether odor.
- Solubility: BH is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether and benzene, but insoluble in water.
- Stability: Under normal conditions, BTH is relatively stable, but spontaneous combustion or explosion may occur at high temperatures, pressures, or when exposed to oxygen.
Use:
- As a solvent: Dibutyl sulfide is often used as a solvent, especially in organic synthesis reactions.
- Preparation of other compounds: BTHL can be used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other organic compounds.
- Catalyst for organic synthesis: Dibutyl sulfide can also be used as a catalyst for organic synthesis reactions.
Method:
- General preparation method: Dibutyl sulfide can be prepared by the reaction of 1,4-dibutanol and hydrogen sulfide.
- Advanced preparation: In the laboratory, it can also be prepared by Grignard reaction or thionyl chloride synthesis.
Safety Information:
- Effects on the human body: BTH can enter the body through inhalation and skin contact, which may cause eye irritation, respiratory irritation, skin allergies, and central nervous system depression. Direct contact should be avoided and adequate ventilation should be ensured.
- Fire and explosion hazards: BTH may spontaneously ignite or explode at high temperatures, pressures, or when exposed to oxygen. Care should be taken to avoid ignition and electrostatic discharge, and store in an airtight container.
- Toxicity: BTH is toxic to aquatic life and should be avoided for release into the environment.