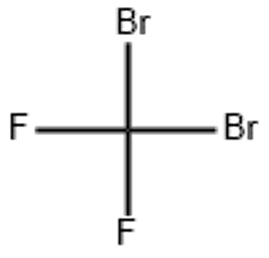
Dibromodifluoromethane (CAS# 75-61-6)
| Risk Codes | R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. R59 – Dangerous for the ozone layer |
| Safety Description | S37/39 – Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S59 – Refer to manufacturer / supplier for information on recovery / recycling. |
| UN IDs | 1941 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | PA7525000 |
| HS Code | 29034700 |
| Hazard Note | Irritant |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| Packing Group | III |
| Toxicity | A 15-min exposure to 6,400 and 8,000 ppm were fatal to rats and mice, respectively (Patnaik, 1992). |
Introduction
Dibromodifluoromethane (CBr2F2), also known as halothane (halothane, trifluoromethyl bromide), is an organic compound. The following is an introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of dibromodifluoromethane:
Quality:
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Solubility: soluble in ethanol, ether and chloride, slightly soluble in water
- Toxicity: has an anesthetic effect and can lead to central nervous system depression
Use:
- Anesthetics: Dibromodifluoromethane, once widely used for intravenous and general anesthesia, has now been replaced by more advanced and safe anesthetics.
Method:
The preparation of dibromodimomethane can be carried out by the following steps:
Bromine is reacted with fluorine at high temperatures to give fluorobromide.
Fluorobromide is reacted with methane under ultraviolet radiation to produce dibromodifluoromethane.
Safety Information:
- Dibromodifluoromethane has anesthetic properties and should be used with caution, especially without professional guidance.
- Long-term exposure to dibromodifluoromethane may have adverse effects on the liver.
- May cause irritation if it gets into the eyes, skin, or respiratory system.
- When using dibromodifluoromethane, flame or high temperature situations should be avoided as it is flammable.
- When using dibromodifluoromethane, follow proper laboratory practices and personal protective measures.