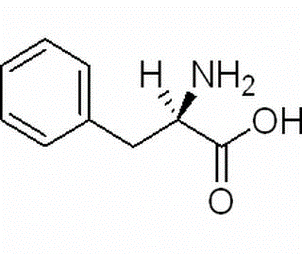
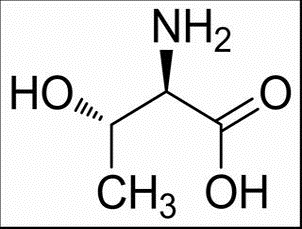
D-2-Amino-3-phenylpropionic acid(CAS# 673-06-3)
| Risk Codes | 34 – Causes burns |
| Safety Description | S24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S27 – Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | AY7533000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29224995 |
| Hazard Note | Irritant |
| Toxicity | TDLo orl-hmn: 500 mg/kg/5W-I:GIT JACTDZ 1(3),124,82 |
Introduction
D-phenylalanine is a protein raw material with the chemical name D-phenylalanine. It is formed from the D-configuration of phenylalanine, a natural amino acid. D-phenylalanine is similar in nature to phenylalanine, but it has different biological activities.
It can be used as a raw material in medicines, health products and nutritional supplements to improve the function of the central nervous system and regulate chemical balance in the body. It is also used in the synthesis of compounds with antitumor and antimicrobial activities.
The preparation of D-phenylalanine can be carried out by chemical synthesis or biotransformation. Chemical synthesis methods typically use enantioselective reactions to obtain products with D configurations. The biotransformation method uses the catalytic action of microorganisms or enzymes to convert natural phenylalanine into D-phenylalanine.
It is an unstable compound that is susceptible to degradation by heat and light. Excessive intake may cause gastrointestinal upset. In the process of using D-phenylalanine, the dosage should be strictly controlled, and relevant safety operating procedures should be followed. For individual people who are allergic to D-phenylalanine or have abnormal phenylalanine metabolism, it should be avoided or used under the guidance of a doctor.