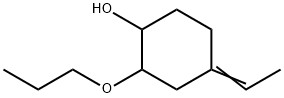
Cyclohexanol, 4-ethylidene-2-propoxy-(CAS#2101609-63-4/1631145-48-6/1631145-49-7/2101609-62-3)
Cyclohexanol, 4-ethylidene-2-propoxy-(CAS#2101609-63-4/1631145-48-6/1631145-49-7/2101609-62-3)
Physical
Appearance: Usually may be a colorless to pale yellow liquid. Most organic compound liquids are colorless in their pure state, and the yellowish color may be due to the presence of small amounts of impurities or a slight oxidation reaction during storage.
Odor: May have a peculiar smell of organic compounds. Due to the presence of cyclohexanol structure, it may have an alcohol-like odor, while the presence of propoxy and ethylene groups may also give it some other odor characteristics.
Solubility: According to the principle of similar miscibility, it may be soluble in polar organic solvents, such as ethanol, methanol, etc., to a certain extent, due to the hydroxyl and ether bonds contained in the molecule. At the same time, due to the presence of a long carbon chain part, it can also be dissolved in some non-polar organic solvents, such as n-hexane and cyclohexane. Solubility in water may be relatively limited as it has a comparatively more non-polar part.
Boiling point and melting point: The specific boiling point and melting point need to be determined by experiments or consult more specialized literature. However, it is speculated that the boiling point may be high due to the cyclic structure and multiple functional groups in its molecular structure. The melting point can be affected by molecular symmetry and intermolecular forces.
Chemical properties
Stability: At room temperature and pressure, it may have a certain degree of stability under general storage conditions. However, chemical reactions may occur in the presence of high temperatures, strong acids, strong alkalis, or strong oxidants. For example, hydroxyl groups may undergo dehydration reactions under acidic conditions, and ethylene double bonds may be oxidized or additions may occur.
Reactivity: The hydroxyl group in the molecule is an active functional group that can undergo esterification reaction, oxidation reaction, etc. For example, it can react with carboxylic acids to form esters, which can be oxidized to ketones or carboxylic acids under the action of suitable oxidants. The 4-position ethylene double bond can be added to hydrogen, halogen, etc., to change the structure and properties of the molecule. The propoxy group at position 2 may also react under certain conditions, such as the cleavage of ether bonds.
use
Organic synthesis intermediates: due to their multiple active functional groups and special structures, they can be used as intermediates in organic synthesis. It is used to synthesize organic compounds with special structures and functions, and may play a role in drug synthesis, fragrance synthesis and other fields. For example, by modifying hydroxyl, ethylene, and propoxy groups, it is possible to construct molecules with pharmacological activity or compounds with special aromas.
Potential applications in the field of materials science: In the field of materials science, its structural characteristics may make it a potential application in the synthesis of some functional materials. For example, in polymer materials, it can be used as a monomer or modifier to give the material new properties, such as flexibility, solubility or optical properties, through polymerization or modification reactions.