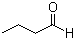
Butyraldehyde(CAS#123-72-8)
| Hazard Symbols | F – Flammable |
| Risk Codes | R11 – Highly Flammable |
| Safety Description | S9 – Keep container in a well-ventilated place. S29 – Do not empty into drains. S33 – Take precautionary measures against static discharges. S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. |
| UN IDs | UN 1129 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | ES2275000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 13-23 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 2912 19 00 |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | Single-dose LD50 orally in rats: 5.89 g/kg (Smyth) |
Introduction
chemical properties
Colorless transparent flammable liquid with asphyxiating aldehyde smell. Slightly soluble in water. Miscible with ethanol, ether, ethyl acetate, acetone, toluene, a variety of other organic solvents and oils.
Use
Used in organic synthesis and a raw material for making spices
Use
GB 2760-96 specifies edible spices that are allowed to be used. Mainly used to prepare bananas, caramel and other fruit flavors.
Use
butyraldehyde is an important intermediate. n-butanol can be produced by hydrogenation of n-butanal; 2-ethylhexanol can be produced by condensation dehydration and then hydrogenation, and n-butanol and 2-ethylhexanol are the main raw materials of plasticizers. n-butyric acid can be produced by oxidation of n-butyric acid; trimethylolpropane can be produced by condensation with formaldehyde, which is a plasticizer for synthesis of alkyd resin and a raw material for air drying oil; condensation with phenol to produce oil-soluble resin; condensation with urea can produce alcohol-soluble resin; products condensed with polyvinyl alcohol, butylamine, thiourea, diphenylguanidine or methyl carbamate are raw materials and, condensation with various alcohols is used as a solvent for celluloid, resin, rubber and pharmaceutical products; the pharmaceutical industry is used to make “Mianerton”, “pyrimethamine”, and amylamide.
Use
Rubber glue, rubber accelerator, synthetic resin ester, manufacturing butyric acid, etc. Its hexane solution is a reagent for determining ozone. Used as a solvent for lipids, also used in the preparation of flavors and fragrances and as a preservative.
Production method
at present, the production methods of butyraldehyde adopt the following methods: 1. propylene carbonyl synthesis method propylene and synthesis gas carry out carbonyl synthesis reaction in the presence of Co or Rh catalyst to generate n-butyraldehyde and isobutyraldehyde. Due to the different catalysts and process conditions used, it can be divided into high-pressure carbonyl synthesis with cobalt carbonyl as catalyst and low-pressure carbonyl synthesis with rhodium carbonyl phosphine complex as catalyst. The high pressure method has high reaction pressure and many by-products, thus increasing the production cost. The low-pressure carbonyl synthesis method has low reaction pressure, positive isomer ratio of 8-10:1, less by-products, high conversion rate, low raw materials, low power consumption, simple equipment, short process, showing excellent economic effects and rapid development. 2. Acetaldehyde condensation method. 3. Butanol oxidative dehydrogenation method uses silver as a catalyst, and butanol is oxidized by air in one step, and then the reactants are condensed, separated, and rectified to obtain the finished product.
Production method
It is obtained by dry distillation of calcium butyrate and calcium formate.
The vapor is obtained by dehydrogenation of the catalyst.
category
flammable liquids
Toxicity classification
Poisoning
acute toxicity
oral-rat LD50: 2490 mg/kg; Abdominal-mouse LD50: 1140 mg/kg
Stimulus data
skin-rabbit 500 mg/24 hours severe; Eyes-rabbit 75 micrograms severe
explosive hazard characteristics
It can be exploded when mixed with air; it reacts violently with chlorosulfonic acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and fuming sulfuric acid
flammability hazard characteristics
It is flammable in case of open flames, high temperatures, and oxidants; combustion produces irritating smoke
storage and transportation characteristics
The warehouse is ventilated and dry at low temperature; stored separately from oxidants and acids
Fire extinguishing agent
Dry powder, carbon dioxide, foam
occupational standards
STEL 5 mg/m3