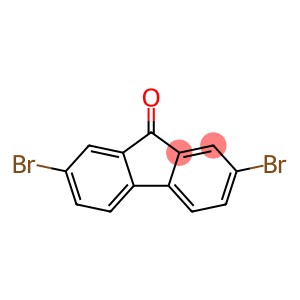
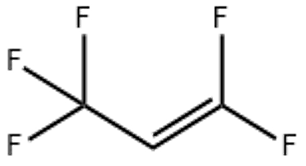
| In vitro study |
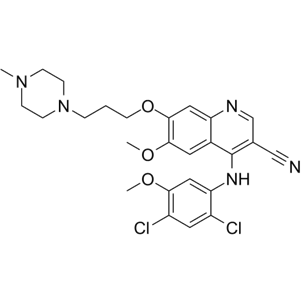
Bosutinib has a higher selectivity for Src than non-Src family kinases, with an IC50 of 1.2 nM, and effectively inhibits Src-dependent cell proliferation, with an IC50 of 100 nM. Bosutinib significantly inhibited the proliferation of Bcr-Abl-positive leukemia cell lines KU812, K562, and MEG-01 but not Molt-4, HL-60, Ramos, and other leukemia cell lines, with IC50 of 5 nM, 20 nM, respectively, and 20 nM, more effective than STI-571. Similar to STI-571, Bosutinib acts on Abl-MLV transforming fibers and has proliferative activity with an IC50 of 90 nM. At concentrations of 50 nM, 10-25 nM, and 200 nM, respectively, Bosutinib excised Bcr-Abl and STAT5 in CML cells and v-Abl tyrosine phosphorylation expressed in fibers, this results in inhibition of phosphorylation of Bcr-Abl downstream signaling Lyn/Hck. Although it can not inhibit the proliferation and survival of breast cancer cells, it can significantly reduce the movement and invasion of breast cancer cells, IC50 is 250 nM, and improve the intercellular adhesion and membrane localization of β-catenin. |
| In vivo study |
Bosutinib was effective in nude mice bearing Src-transformed fiber xenografts and HT29 xenografts at a dose of 60 mg/kg per day, with T/C values of 18% and 30%, respectively. Oral administration of Bosutinib to mice for 5 days significantly inhibited the growth of K562 tumors in a dose-dependent manner. Large tumors were eradicated at a dose of 100 mg/kg, treatment at a dose of 150 mg/kg removed tumors with no toxicity. Compared with the effect on HT29 transplanted tumor, Bosutinib at a dose of 75 mg/kg, twice a day, could inhibit tumor growth in nude mice bearing Colo205 transplanted tumor, there was no higher effect after increasing the dose, but the 50 mg/kg dose had no effect. |