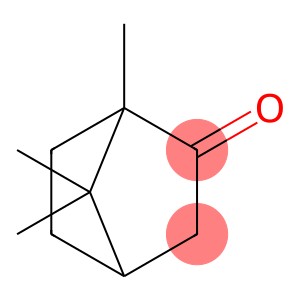
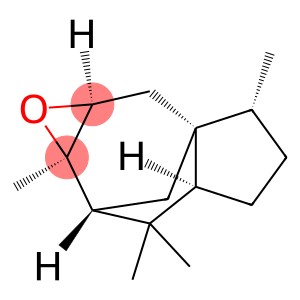
bornan-2-one CAS 76-22-2
| Risk Codes | R11 – Highly Flammable R22 – Harmful if swallowed R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. R20/21/22 – Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| Safety Description | S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S37/39 – Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection |
| UN IDs | UN 2717 4.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | EX1225000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29142910 |
| Hazard Class | 4.1 |
| Packing Group | III |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in mice: 1.3 g/kg (PB293505) |
Introduction
Camphor is an organic compound with the chemical name 1,7,7-trimethyl-3-nitroso-2-cyclohepten-1-ol. The following is a brief introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of camphor:
Quality:
- It is white crystalline in appearance and has a strong camphor smell.
- Soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether and chloroform, slightly soluble in water.
- Has a pungent smell and spicy taste, and has an irritating effect on the eyes and skin.
Method:
- Camphor is mainly extracted from the bark, branches and leaves of the camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora) by distillation.
- The extracted tree alcohol undergoes treatment steps such as dehydration, nitration, lysis, and cooling crystallization to obtain camphor.
Safety Information:
- Camphor is a toxic compound that can cause poisoning when exposed to excessive amounts.
- Camphor is irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract and should be avoided in direct contact.
- Long-term exposure to or inhalation of camphor may cause problems with the respiratory and digestive systems.
- Wear appropriate protective gloves, glasses and masks when using camphor, and ensure a well-ventilated environment.
- Chemistry and safety protocols should be used for camphor before use, and it should be stored properly to prevent accidents.