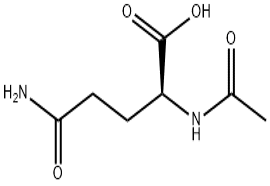
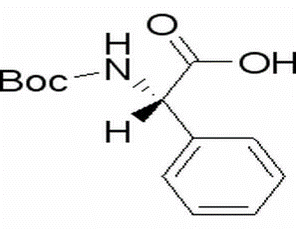
BOC-L-Phenylglycine(CAS# 2900-27-8)
| Safety Description | S22 – Do not breathe dust. S24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 2924 29 70 |
Introduction
N-Boc-L-Phenylglycine is an organic compound that is formed by the formation of a chemical bond between the amino group (NH2) of glycine and the carboxyl group (COOH) of benzoic acid. Its structure contains a protective group (Boc group), which is tert-butoxycarbonyl group, which is used to protect the reactivity of the amino group.
N-Boc-L-phenylglycine has the following properties:
- Appearance: White crystalline solid
- Solubility: Soluble in some organic solvents, such as dimethylformamide (DMF), dichloromethane, etc
N-Boc-L-phenylglycine is commonly used in multi-step reactions in organic synthesis, especially for the synthesis of peptide compounds. The Boc protecting group can be deprotected by acidic conditions, so that the amino group can be reactive and then carry out subsequent reactions. N-Boc-L-phenylglycine can also be used as a derivative for the construction of chiral centers in peptide synthesis.
The preparation of N-Boc-L-phenylglycine is mainly carried out by the following steps:
Glycine is esterified with benzoic acid to obtain benzoic acid-glycinate ester.
Using lithium borotrimethyl ether (LiTMP) reaction, the benzoic acid-glycinate ester was protonated and reacted with Boc-Cl (tert-butoxycarbonyl chloride) to obtain N-Boc-L-phenylglycine.
- N-Boc-L-phenylglycine may be irritating to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract and should be avoided during use.
- Personal protective equipment such as laboratory gloves, safety glasses, etc. should be worn during operation.
- It should be performed in a well-ventilated laboratory environment.
- Avoid contact with oxidants and strong acids when storing.
- If swallowed or inhaled, seek medical attention immediately, bring a container of the compound, and provide the necessary safety information to the doctor.



![N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-L-leucine(CAS# 13139-15-6)](https://www.xinchem.com/uploads/BocLLeucine.png)