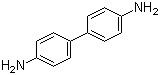
Benzidine(CAS#92-87-5)
| Risk Codes | R45 – May cause cancer R22 – Harmful if swallowed R50/53 – Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. R52/53 – Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. R39/23/24/25 - R23/24/25 – Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R11 – Highly Flammable R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. R20/21/22 – Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R51/53 – Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. R67 – Vapors may cause drowsiness and dizziness |
| Safety Description | S53 – Avoid exposure – obtain special instructions before use. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S60 – This material and its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste. S61 – Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets. S36/37 – Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S7 – Keep container tightly closed. S36 – Wear suitable protective clothing. S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. |
| UN IDs | UN 1885 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DC9625000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 8 |
| HS Code | 29215900 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | Acute oral LD50 for mice 214 mg/kg, rats 309 mg/kg (quoted, RTECS, 1985). |
Introduction
Benzidine (also known as diphenylamine) is an organic compound. The following is an introduction to its nature, use, manufacturing methods and safety information:
Quality:
- Appearance: Benzidine is a white to light yellow crystalline solid.
- Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols, ethers, etc.
- Symbol: It is an electrophile that has the properties of an electrophilic substitution reaction.
Use:
- Benzidine is widely used in the field of organic synthesis. It can be used as a raw material and synthetic intermediate for chemicals such as dyes, pigments, plastics, etc.
Method:
- Benzidine is traditionally prepared by dinitrobiphenyl reduction, radiation elimination of haloaniline, etc.
- Modern preparation methods include organic synthesis of aromatic amines, such as the reaction of the substrate diphenyl ether with amino alkanes.
Safety Information:
- Benzidine is toxic and can cause irritation and damage to the human body.
- When handling benzidine, care should be taken to avoid skin contact and inhalation, and protective equipment such as gloves, protective glasses, and protective masks should be worn if necessary.
- When benzidine comes into contact with the skin or eyes, it should be rinsed immediately with plenty of water.
- When storing and using benzidine, take care to avoid contact with organic matter and oxidants to prevent fire or explosion.