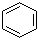
Benzene;Benzol Phenyl hydride Cyclohexatriene Coalnaphtha;Phene (CAS#71-43-2)
| Risk Codes | R45 – May cause cancer R46 – May cause heritable genetic damage R11 – Highly Flammable R36/38 – Irritating to eyes and skin. R48/23/24/25 - R65 – Harmful: May cause lung damage if swallowed R39/23/24/25 - R23/24/25 – Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| Safety Description | S53 – Avoid exposure – obtain special instructions before use. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S36/37 – Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S7 – Keep container tightly closed. |
| UN IDs | UN 1114 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CY1400000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 3-10 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 2902 20 00 |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in young adult rats: 3.8 ml/kg (Kimura) |
Introduction
Benzene is a colorless and transparent liquid with a special aromatic odor. The following is an introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of benzene:
Quality:
1. Benzene is highly volatile and flammable, and can form an explosive mixture with oxygen in the air.
2. It is an organic solvent that can dissolve many organic matter, but is insoluble in water.
3. Benzene is a conjugated aromatic compound with a stable chemical structure.
4. The chemical properties of benzene are stable and not easy to be attacked by acid or alkali.
Use:
1. Benzene is widely used as an industrial raw material for the manufacture of plastics, rubber, dyes, synthetic fibers, etc.
2. It is an important derivative in petrochemical industry, used to manufacture phenol, benzoic acid, aniline and other compounds.
3. Benzene is also commonly used as a solvent for organic synthesis reactions.
Method:
1. It is obtained as a by-product in the refining process of petroleum.
2. It is obtained by the dehydration reaction of phenol or the cracking of coal tar.
Safety Information:
1. Benzene is a toxic substance, and long-term exposure to or inhalation of high concentrations of benzene vapor will cause serious health risks to the human body, including carcinogenicity.
2. When using benzene, it is necessary to maintain good ventilation conditions to ensure that the operation is carried out in an appropriate environment.
3. Avoid skin contact and inhalation of benzene vapor, and wear personal protective equipment such as protective gloves and respirators.
4. Eating or drinking benzene-containing substances will lead to poisoning, and safety operating procedures should be strictly observed.
5. Waste benzene and the waste involved in benzene should be disposed of in accordance with appropriate laws and regulations to avoid environmental pollution and harm.