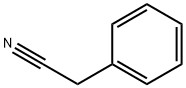
Benzeneacetonitrile(CAS#140-29-4)
| Hazard Symbols | T – Toxic |
| Risk Codes | R23/24/25 – Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. |
| Safety Description | S23 – Do not breathe vapour. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) |
| UN IDs | UN 2470 |
Benzeneacetonitrile(CAS#140-29-4)
Benzeneacetonitrile, CAS number 140-29-4, is unique in many aspects of chemistry.
From the chemical structure, it is composed of a benzene ring linked to an acetonitrile group. The benzene ring has a large π bond conjugation system, which gives the molecule stability and a unique electron cloud distribution, which makes it have a certain aromaticity. The acetonitrile group introduces the strong polarity and reactivity of the cyano group, which makes the whole molecule not only have the relative inertness and hydrophobicity brought by the benzene ring, but also provide rich possibilities for organic synthesis because the cyano group can participate in a variety of nucleophilic and electrophilic reactions. It usually appears as a colorless to light yellow liquid in appearance, and this liquid form is convenient for transfer and purification through routine operations such as liquid separation and distillation in laboratory and industrial synthesis scenarios. In terms of solubility, it can be better soluble in organic solvents, such as ether, chloroform and other non-polar or weakly polar solvents, while in water solubility is poor, which is closely related to molecular polarity, and also determines its application selection in different reaction systems.
It is an important intermediate in organic synthesis applications. Based on their structural properties, a variety of chemical reactions can occur to construct complex compounds. For example, through the hydrolysis reaction of cyanogroup, phenylacetic acid can be prepared, which is used in the pharmaceutical field to synthesize a variety of drugs, such as the side chain modification of penicillin antibiotics; In the spice industry, it is the key raw material for the preparation of floral spices such as roses and lily of the valley. In addition, the reduction reaction of cyano can also be used to convert it into benzylamine compounds, and benzylamine derivatives are widely used in the field of pesticides and dyes, and are used to develop new high-efficiency pesticides, dyes with bright colors and high fastness.
In terms of preparation method, acetophenone is often used as raw material in industry, and it is prepared by a two-step reaction of oxime and dehydration. First, acetophenone reacts with hydroxylamine to form acetophenone oxime, which is then transformed into Benzeneacetonitrile under the action of a dehydrator, and in the process, researchers continue to optimize the reaction conditions, including adjusting the reaction temperature and controlling the amount of dehydrator, so as to improve the yield, reduce the cost, and ensure the demand for large-scale production. With the innovation of organic synthesis technology, the optimization of the synthesis route of Benzeneacetonitrile focuses on environmental protection and atomic economy, striving to reduce waste emissions, improve resource utilization efficiency, contribute to the sustainable development of the chemical industry, and further expand its application potential.