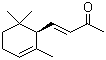
alpha-Ionone(CAS#127-41-3)
| Risk Codes | R42/43 – May cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact. |
| Safety Description | S24/25 – Avoid contact with skin and eyes. |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | EN0525000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29142300 |
alpha-Ionone(CAS#127-41-3) information
Violet ketone, also known as benzophenone, is an organic compound. Here are some safety information about ionone:
1. Toxicity: Violet ketone has certain toxicity to the human body. It may cause damage to the central nervous system and liver, and may have adverse effects on the reproductive system and embryos.
2. Inhalation hazard: Inhaling the vapor or dust of ionone may cause discomfort symptoms such as dizziness, drowsiness, coughing, and difficulty breathing. Long term exposure may cause damage to the central nervous system.
3. Contact hazard: Violet ketone can be absorbed through the skin. Long term or extensive contact may cause skin and eye irritation. Appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves and safety goggles should be worn when handling ionone.
4. Fire extinguishing measures: In case of leakage or fire, use dry powder, foam or carbon dioxide to extinguish the fire. Avoid using water, as violet ketone reacts with water to produce flammable gases.
5. Waste disposal: Dispose of waste violet ketone properly in accordance with local regulations and rules. Do not discharge it into the sewer or garbage bin.
6. Storage precautions: Violet ketone should be stored in a cool, dry, well ventilated place, away from sources of fire and oxidants.
These information are for reference only. If further use or processing of ionone is required, please refer to the relevant safety data sheet and consult a professional.
nature
Violet ketone, also known as linaylketone, is a natural ketone compound. It is the main component of the aroma of violet flowers.
Violet ketone is a colorless to pale yellow oily liquid that is volatile at room temperature.
Violet ketone is soluble in alcohol and ether solvents, and slightly soluble in water. Its density is relatively low, with a density of 0.87 g/cm ³. It is sensitive to light and can absorb ultraviolet rays.
Violet ketone can be oxidized to ketone alcohols or acids in chemical reactions, and can be reduced to alcohols through hydrogenation reduction reactions. It can undergo alkylation and esterification reactions with many compounds.
Application and synthesis method
Violet ketone (also known as purple ketone) is an aromatic ketone compound. It has special fragrance and is often used in perfume and perfume industry. The following is an introduction to the uses and synthesis methods of ionone:
Purpose:
Perfume and spice: the fragrance characteristics of ionone, which is widely used in perfume and spice industry to manufacture violet fragrance products.
Synthesis method:
The synthesis of ionone is generally achieved through the following two methods:
Oxidation of Nucleobenzene: Nucleobenzene (a benzene ring with a methyl substituent) is subjected to an oxidation reaction, such as using an oxidizing acid or an acidic potassium permanganate solution, to generate ionone.
Coupling of Pyrylbenzaldehyde: Pyrylbenzaldehyde (such as benzaldehyde with pyridine ring substituents in the para or meta position) is reacted with acetic anhydride and other reactants under alkaline conditions to form ionone.