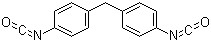
4,4′-Diphenylmethane diisocyanate(CAS#101-68-8)
| Risk Codes | R42/43 – May cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact. R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. R20 – Harmful by inhalation R48/20 - R40 – Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect |
| Safety Description | S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) S36/37 – Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. S23 – Do not breathe vapour. |
| UN IDs | 2206 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | NQ9350000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29291090 |
| Hazard Note | Toxic/Corrosive/Lachrymatory/Moisture Sensitive |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 5000 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit > 9000 mg/kg |
Introduction
Diphenylmethane-4,4′-diisocyanate, also known as MDI. It is an organic compound and is a type of benzodiisocyanate compounds.
Quality:
1. Appearance: MDI is colorless or light yellow solid.
2. Solubility: MDI is soluble in organic solvents such as chlorinated hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons.
Use:
It is used as a raw material for polyurethane compounds. It can react with polyether or polyurethane polyols to form polyurethane elastomers or polymers. This material has a wide range of applications in construction, automotive, furniture, and footwear, among others.
Method:
The method of diphenylmethane-4,4′-diisocyanate is mainly to react aniline with isocyanate to obtain aniline-based isocyanate, and then go through diazotization reaction and denitrification to obtain the target product.
Safety Information:
1. Avoid contact: Avoid direct skin contact and be equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves, goggles and protective clothing.
2. Ventilation: Maintain good ventilation conditions during operation.
3. Storage: When storing, it should be sealed and kept away from fire sources, heat sources and places where ignition sources occur.
4. Waste disposal: Waste should be properly treated and disposed of, and should not be dumped at will.
When handling chemical substances, they should be handled in strict accordance with laboratory operating procedures and safety guidelines, and in accordance with relevant laws and regulations.