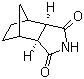
“(3aR, 4S, 7R, 7aS)-hexahydro-1H-4, 7- methanoisoindole-1.3(2H)-dione(CAS#14805-29-9)”
(3aR, 4S, 7R, 7aS)-hexahydro-1H-4, 7- methanoisoindole-1.3(2H)-dione(CAS#14805-29-9)
Physicochemical properties
Appearance: Generally white or off-white crystalline powder.
Melting Point: There is usually a specific melting point range that can be used for purity identification, etc., and the specific melting point data may be around 150 – 160°C, but it may vary depending on the experimental conditions and purity.
Solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in some organic solvents, such as methylene chloride, chloroform, acetone, etc. This is due to the fact that its molecule contains certain polar groups (carbonyl groups) and at the same time has a large non-polar hydrocarbon group part, which causes its solubility in different solvents to exhibit such characteristics.
Stability: Stable at room temperature and pressure, but decomposition or chemical reaction may occur under high temperature, strong acid, strong alkali or strong redox conditions. For example, under acidic conditions, a hydrolysis reaction may occur, causing the amide bond to break.
Synthesis method
The bridge-ring structure of its core can usually be constructed by means of the Diels-Alder reaction. Using suitable dienes and diphiles as raw materials, cycloaddition reactions occur under heating or light conditions to generate intermediates with bridge-ring structures, and then through further functional group conversion reactions, such as amidation and other reactions, carbonyl and other functional groups are introduced to obtain the target product.
It can also be synthesized from some natural products containing similar skeletons through chemical modification and modification.
Fields of application
Pharmaceutical field: its unique structure makes it potentially valuable in drug research and development, and may be used as an important pharmaceutical intermediate for the synthesis of drug molecules with specific biological activities. For example, by introducing different functional groups or side chains into its structure, the activity, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties of drug molecules can be regulated, among others, and can be used to treat a variety of diseases, such as neurological diseases, tumors, etc.
Organic synthesis: As an organic compound with a special structure, it can be used for the research and development of organic synthesis methodology. It can be used as a substrate to participate in various organic reactions, such as nucleophilic substitution, electrophilic addition, redox and other reactions, which provides a research object for exploring new organic synthesis reactions and strategies.
Safety Information
Toxicity: There may not be comprehensive and detailed toxicity data at this time, but as an organic compound, it may have some potential toxicity. It may exhibit certain acute or chronic toxicity in animal experiments, affecting the organs and systems of organisms.
Precautions for operation: In laboratory operations, it should be carried out in a well-ventilated environment, wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, etc., to avoid skin contact and inhalation of dust. Because it may be irritating, it should be rinsed with plenty of water immediately after contact with the skin, and if it accidentally gets into the eyes, it should be rinsed with plenty of saline immediately and seek medical attention.