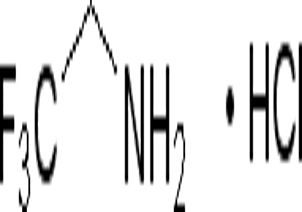2 -phenyl-Hexanenitrile(CAS#3508-98-3)
| Risk Codes | R22 – Harmful if swallowed R50/53 – Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
| Safety Description | S23 – Do not breathe vapour. S60 – This material and its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste. S61 – Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets. |
2 -phenyl-Hexanenitrile(CAS#3508-98-3)
Production method
α-n-butylphenylacetonitrile is a raw material for organic synthesis, and its production method usually involves two steps: benzylation and cyanidation.
The benzyl and n-butyl compounds are reacted by benzylation. This can be achieved by reacting styrene and bromobutane under alkaline conditions. Under alkaline conditions, the double bonds in styrene undergo a substitution reaction with bromobutane to form a benzyl compound, α-bromophenyl ethane.
α-bromophenyethane is then cyanidated with sodium cyanide in an alcohol solvent such as methanol or ethanol. In this reaction, the bromine group is replaced by a cyano group to form α-butylphenylacetonitrile.
This synthesis method can be used in both laboratory and industrial production. In industrial production, it is also important to ensure the control of reaction conditions and the improvement of product purity. quality
α-n-butylphenylacetonitrile is an organic compound. It has a colorless liquid appearance and a special aromatic odor.
ABEN has good solubility, it can be soluble in many organic solvents, such as ethanol, ethers and benzene. It has less solubility in water.
ABEN is a weakly acidic compound that reacts weakly in aqueous solution. It can react with aldehydes and ketones through dehydration condensation reaction to generate corresponding alkene compounds.
Care should be taken to follow the safe operating procedures when using, avoid contact with the skin and inhalation of its vapors, and avoid it entering the eyes and digestive tract.


![1-[1-(3,3-dimethylcyclohexyl)ethyl] 3-ethyl propanedioate(CAS#478695-70-4)](https://www.xinchem.com/uploads/1-1-33-dimethylcyclohexylethyl-3-ethyl-propanedioate.jpg)