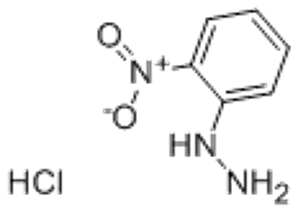2-MethylPhenylHydrazine Hydrochloride(CAS# 56413-75-3)
| Risk Codes | R20 – Harmful by inhalation R21 – Harmful in contact with skin R36 – Irritating to the eyes R37 – Irritating to the respiratory system R22 – Harmful if swallowed |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S44 - S28 – After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of soap-suds. |
| UN IDs | 1325 |
| RTECS | MV8230000 |
| HS Code | 29280000 |
| Hazard Note | Harmful |
| Hazard Class | 4.1 |
| Packing Group | II |
Introduction
2-nitrophenylhydrazine hydrochloride. The following is an introduction to its properties, uses, manufacturing methods and safety information:
Quality:
- Appearance: White crystalline or crystalline powder.
- Solubility: soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohols and ethers.
- Chemical properties: good stability, can have some organic reactions with other compounds.
Use:
- 2-Nitrophenylhydrazine hydrochloride is mainly used in the synthesis of pesticides and the preparation of explosives.
- It can be used as an intermediate of the pesticide timmodine and as a precursor to the explosive preparation hexanitroglutarate.
Method:
2-Nitrophenylhydrazine hydrochloride can be prepared by the following steps:
1. 2-nitrophenylhydrazine reacts with hydrochloric acid to form 2-nitrophenylhydrazine hydrochloride.
2. The target product is obtained through crystallization, filtration and drying.
Safety Information:
- 2-Nitrophenylhydrazine hydrochloride is relatively stable under normal operating conditions, but creates an explosion hazard under high temperatures, lasers, or other heat sources.
- Wear appropriate protective equipment such as lab gloves, goggles, and a lab coat when operating.
- Avoid contact with strong acids, strong oxidants, etc.
- Avoid inhaling dust or contact with the skin to avoid irritation or allergic reactions.
- It should be operated in a well-ventilated laboratory environment to avoid inhaling its vapors. If inhaled, move to fresh air and seek medical attention.