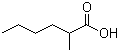2-Methylhexanoic acid(CAS#4536-23-6)
| Hazard Symbols | C – Corrosive |
| Risk Codes | 34 – Causes burns |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) |
| UN IDs | UN 3265 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | MO8400600 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29159080 |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| Packing Group | III |
Introduction
2-Methylhexanoic acid is an organic compound. The following is a brief introduction to the properties, uses, preparation methods and safety information of 2-methylhexanoic acid:
Quality:
- Appearance: 2-Methylhexanoic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor.
- Solubility: Soluble in water and common organic solvents.
Use:
- 2-Methylhexanoic acid is widely used in the manufacture of chemical products such as plastics, dyes, rubber, and coatings.
Method:
- 2-Methylhexanoic acid can be synthesized by oxidation of heterocyclic amine catalysts. The catalyst is usually a transition metal salt or similar compound.
- The other method is obtained by esterification of adipic acid, which requires the use of esterifiers and acid catalysts.
Safety Information:
- 2-Methylhexanoic acid is an irritant that may cause irritation and inflammation in contact with the skin and eyes, and appropriate precautions should be taken.
- During use and storage, contact with oxidants and strong acids should be avoided to avoid dangerous reactions.
- In the event of an accidental leak, appropriate measures should be taken, such as wearing protective gear, safe disposal and proper disposal of waste.
When handling chemicals, always follow proper laboratory safety practices and relevant laws and regulations.