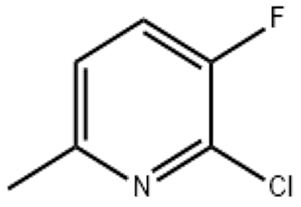
2-Chloro-3-fluoro-6-picoline(CAS# 374633-32-6)
Introduction
Appearance: Usually colorless to light yellow liquid, this appearance characteristics imply that it may be sensitive to light and heat, and it is necessary to take measures to avoid light and temperature control during storage and transportation, such as using brown glass bottles and storing them in a cool warehouse to prevent further color deepening and deterioration.
Solubility: The compound has good solubility in common organic solvents, such as toluene and dichloromethane, follows the principle of similar solubility, and has an affinity with organic solvents by virtue of the hydrophobic part of the molecule; However, the solubility in water is low, and the strong hydrogen bonding between water molecules is difficult to be effectively broken by the molecule, making it difficult to disperse it.
Boiling point and density: Boiling point data is closely related to its volatility and can provide key parameters for operations such as distillation and purification, but unfortunately the specific boiling point value has not been widely disclosed. Its density is slightly higher than that of water, and understanding the density can help to accurately estimate the volume-mass conversion relationship in experimental operations or industrial processes such as liquid transfer and precise metering.
Chemical properties
Substitution reaction: The chlorine atom and fluorine atom in the molecule are the potential reactive sites. In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, strong nucleophiles can attack the sites where chlorine and fluorine atoms are located, replace the corresponding atoms, and generate new pyridine derivatives. For example, it has been combined with some nitrogen-containing and sulfur-containing nucleophiles to develop a series of nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds with more complex structures for drug discovery or material synthesis.
Redox reaction: the pyridine ring itself is relatively stable, but when strong oxidants, such as potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide are paired with acidic conditions, oxidation may occur, resulting in the destruction or modification of the pyridine ring structure; Conversely, with a suitable reducing agent, such as metal hydrides, it is theoretically possible to hydrogenation of intramolecular unsaturated bonds.
Fourth, the synthesis method
The common synthesis path is to start from simple pyridine derivatives and gradually construct the target structure through halogenation and fluorination reactions. The starting material pyridine compounds are first selectively methylated and the methyl groups are introduced at the same time; Then use halogenation reagents, such as chlorine and liquid chlorine, with suitable catalysts and reaction conditions, to achieve the introduction of chlorine atoms; Finally, fluorinated reagents, such as Selectfluor, were used to accurately fluorinate the target site to obtain 2-chloro-3-fluoro-6-methylpyridine.
Uses
Drug synthesis intermediates: its unique structure is loved by medicinal chemists, and it is a high-quality intermediate for the development of new antibacterial, antiviral, and antitumor drugs. The electronic properties and spatial structure of pyridine rings and their substituents can specifically bind to target proteins in vivo, and are expected to be transformed into active ingredients with excellent efficacy after subsequent multi-step modification.
Materials science: In the field of organic material synthesis, it can be used to manufacture functional polymer materials, fluorescent materials, etc., by virtue of its ability to accurately introduce chlorine, fluorine atoms and pyridine structures, endow materials with special electrical and optical properties, and promote the development of cutting-edge technologies such as smart materials and display materials.