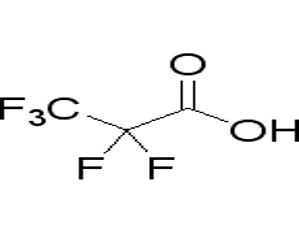
2 2 3 3 3-Pentafluoropropanoic acid(CAS# 422-64-0)
| Hazard Symbols | C – Corrosive |
| Risk Codes | R20 – Harmful by inhalation R34 – Causes burns |
| Safety Description | S26 – In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S36/37/39 – Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection. S45 – In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.) |
| UN IDs | UN 3265 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UF6475000 |
| FLUKA BRAND F CODES | 3 |
| TSCA | T |
| HS Code | 29159080 |
| Hazard Note | Corrosive |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| Packing Group | III |
| Toxicity | LD10 orl-rat: 750 mg/kg GTPZAB10(3),13,66 |
Introduction
Pentafluoropropionic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It is a strong acid that reacts with water to form hydrofluoric acid. Pentafluoropropionic acid is a strong oxidizing agent that reacts with many organic substances and metals. It decomposes at high temperatures and is corrosive.
Pentafluoropropionic acid has a wide range of uses in the chemical industry. It is also used in the preparation of polymer materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene and polymerized perfluoropropylene. Pentafluoropropionic acid is also used as an electroplating, rust inhibitor and surface treatment agent.
There are several methods for the preparation of pentafluoropropionic acid, one of which is commonly obtained by the reaction of boron trifluoride and hydrogen fluoride. Hydrogen fluoride gas is passed into a solution of boron trifluoride and reacted at an appropriate temperature to finally obtain pentafluoropropionic acid.
It is intensely corrosive and irritating, causing burns and severe irritation in contact with the skin or eyes. Personal protective equipment such as protective gloves, goggles, and protective clothing should be used during operation. It should be used in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling its vapors. If inhaled, get fresh air immediately and seek medical attention.