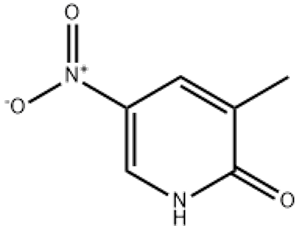
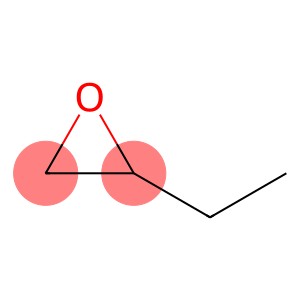
1,2-epoxybutane(CAS#106-88-7)
| Risk Codes | R11 – Highly Flammable R20/21/22 – Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R36/37/38 – Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. R40 – Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect R52/53 – Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. |
| Safety Description | S9 – Keep container in a well-ventilated place. S16 – Keep away from sources of ignition. S29 – Do not empty into drains. S36/37 – Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves. S61 – Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets. S19 - |
| UN IDs | UN 3022 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | EK3675000 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| HS Code | 29109000 |
| Hazard Class | 3.1 |
| Packing Group | II |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 500 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit 1743 mg/kg |
Introduction
1,2-Epibutane is an organic compound. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor at room temperature. The following is an introduction to its main properties, uses, manufacturing methods and safety information:
Properties: It is a flammable liquid that can form an explosive mixture with oxygen. It is also a strong skin irritant and eye irritater.
Use:
1,2-Butyloxide is widely used in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, pesticides and coatings. It is an important intermediate and is often used in organic synthesis to prepare other compounds, such as alcohols, ketones, ethers, etc. It is also used as an ingredient in organic solvents and adhesives.
Method:
1,2-Epibutane can be prepared by the reaction of octanol and hydrogen peroxide. The specific preparation method is to react octanol with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of an appropriate catalyst to generate 1,2-epoxybutane.
Safety Information:
1,2-Epibutane is a hazardous substance with potential hazards such as irritation and teratogenicity. Care should be taken to avoid contact with the skin and inhalation of its vapors during use, and appropriate protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection should be provided if necessary. During storage and handling, care should be taken to prevent ignition and static electricity. Avoid mixing with strong oxidants and acids to avoid dangerous reactions. When disposing of waste, local rules and regulations should be followed.


![2-Amino-5-Cbz-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1,3-thiazolo[5,4-c]pyridine(CAS#1141669-69-3)](https://www.xinchem.com/uploads/AminoCbz.gif)