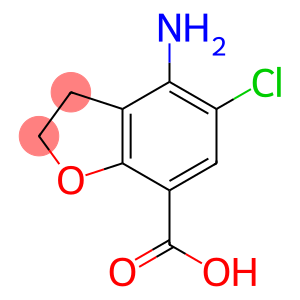
1-Propanone,3-(dimethylamino)-1-(1-naphthalenyl)-, hydrochloride (1:1)(CAS#5409-58-5)
Introduction
3-Dimethylamino-1-(naphthale-1-yl)-1-acetone hydrochloride, also known as DMAP, is an organic compound. The following is an introduction to its nature, use, manufacturing method and safety information:Quality:- Appearance: DMPs are typically white crystals or powdered solids.- Stability: DMAPs are relatively stable at room temperature, but may decompose at high temperatures.- Solubility: DMAP is easily soluble in common organic solvents and insoluble in water.Use:- Catalyst: DMAP is often used as a strong basic catalyst, especially suitable for esterification reactions, deprotection reactions, and anhydrous cyclization reactions. It reduces the reaction time of esterification reactions and increases yields. In organic synthesis, DMAP is also commonly used in the synthesis of compounds such as amides, acid chlorides, and esters.Method:The common preparation method of DMAP is obtained by reacting dimethylamine with 1-(naphthalene-1-yl)-1-acetone in hydrochloric acid solution.Safety Information:- DMAP is an organic substance that is toxic to humans. Direct contact with the skin, eyes, or inhalation of its powder should be avoided. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves, safety glasses, and masks when in use.- DMPs should be stored in an airtight container away from contact with moisture, strong acids, and bases.- When using or handling DMAPs, proper laboratory procedures should be followed and strictly in accordance with the relevant Safety Data Sheets and operating manuals.


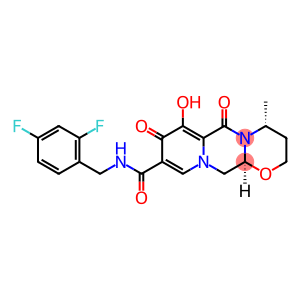
![(4R,12aS)-7-(benzyloxy)-4-Methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-[1,3]oxazino[3,2-d]pyrido[1,2-a]pyrazine-6,8(12H,12aH)-dione(CAS#1206102-09-1)](https://www.xinchem.com/uploads/benzyloxyb.png)